
/ping-command-prompt-92f4acb37dfc4bbc9ac1ae6d99faaa45.png)
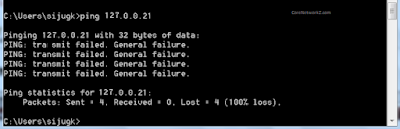
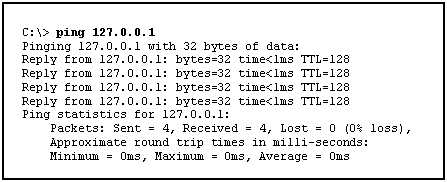
If the loopback interface replies to ping messages, the TCP/IP protocol stack is properly configured. To test whether the TCP/IP stack is properly implemented on the local system, you can send a ping request to the loopback interface. Up to thirty-two IP addresses are supported on a loopback interface. TCP/IP protocol stack provides a loopback interface.
You can configure multiple IP addresses on a loopback interface ( lo0 to lo7). In the same way, if you configure a loopback interface ( lo1) with IP address 172.16.101.8, you cannot configure another loopback interface ( lo2) with IP address 172.16.101.8.
This means that the address cannot be used by a VLAN interface or another loopback interface.įor example, if you configure a VLAN with IP address 172.16.100.8/24, you cannot configure a loopback interface with IP address 172.16.100.8. The maximum number of IP addresses supported on a switch is 2048, which includes all IP addresses configured for both VLANs and loopback interfaces (except for the default loopback IP address 127.0.0.1).Įach IP address that you configure on a loopback interface must be unique in the switch. This is not true, at least on FreeBSD: ping 127.1.1.1 PING 127.1.1.1 (127.1.1.1): 56 data bytes ping: sendto: Cant assign requested address.
#Ping loopback drivers#
It’s the best place to start to ensure that your network drivers and computer are operating correctly. The most commonly used IP address on the loopback device is 127.0.0.1 for IPv4, although any address in the range 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 is mapped to it. Loopback interfaces share the same IP address space with VLAN configurations. A loopback ping is your computer doing a ping test with itself. You can configure a loopback interface only from the CLI you cannot configure a loopback interface from the WebAgent or Menu interface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
